 |
A satellite is any object or body that orbits around another object. An artificial satellite is any human made object designed to orbit the Earth or any other celestial body. The is no where near all about artificial satellites. There is a seemingly overwhelming amount of technology and engineering that goes into building even the simplest artificial satellite. Despite the challenges of constructing an artificial satellite, there are thousands of them orbiting our planet.
In 1957, the Soviet Union launched the world’s first satellite, known as Sputnik. Since then, dozens of countries have launched satellites, with more than 3,000 currently operating spacecraft going around the Earth. There are estimated to be more than 8,000 pieces of space junk; dead satellites or pieces of debris going around the Earth as well. Good news is that, Bangabandhu-1 will be Bangladesh's first satellite. This satellite will stay at 119.1° East longitude. (To know more Click Here)
Satellites can be classified by
their functions. Satellites are launched into space to do a specific job. The
type of satellite that is launched to monitor cloud patterns for a weather
station will be different than a satellite launched to send television signals
across Canada. The satellite must be designed specifically to fulfill its
function.
Below are the names of ten different types of satellites with example-
- Astronomy satellites - Hubble Space Telescope
- Atmospheric Studies satellites - Polar
- Communications satellites - Anik E
- Navigation satellites - Navstar
- Reconaissance satellites - Kennan, Big Bird, Lacrosse
- Remote Sensing satellites - Radarsat
- Search and Rescue satellites - Cospas-Sarsat
- Space Exploration satellites - Galileo
- Weather satellites - Meteosat
- Military satellites- The U.S deafness.

Two
Stations on Earth want to communicate through radio broadcast but are too far
away to use conventional means. The
two stations can use a satellite as a relay station for their communication. One
Earth Station sends a transmission to the satellite. This is called a Up-link. The
satellite Transponder converts the signal and sends it down to the
second earth station. This is called a Down-link.
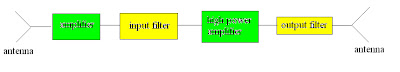
Working process of a satellite is very easy. A antenna, low noise amplifier (because the signal is initially very small), input filters to get rid of any noise from Earth, high power amplifiers to be able to send the signal back to earth, output filter to eliminate noise from satellite hardware and signals adding together, another antenna.
If some part of a
satellite breaks down, but the satellite remains capable of doing useful work,
the satellite owner usually will continue to operate it. In some cases, ground
controllers can repair or reprogram the satellite. In rare instances, space
shuttle crews have retrieved and repaired satellites in space. If the satellite
can no longer perform usefully and cannot be repaired or reprogrammed,
operators from the control center will send a signal to shut it off.
The
advantages of satellite communication are
- The coverage area of a satellite greatly exceeds that of a terrestrial system.
- Transmission cost of a satellite is independent of the distance from the center of the coverage area.
- Satellite to Satellite communication is very precise.
- Higher Bandwidths are available for use.
The disadvantages of satellite communication
- Launching satellites into orbit is costly.
- Satellite bandwidth is gradually becoming used up.
- There is a larger propagation delay in satellite communication than in terrestrial communication.
Reference:
http://viterbivoices.usc.edu/emily/summer-at-boeing/
http://www.universetoday.com/82680/all-about-artificial-satellites/#ixzz2QVtSaj2j
http://viterbivoices.usc.edu/emily/summer-at-boeing/
http://www.universetoday.com/82680/all-about-artificial-satellites/#ixzz2QVtSaj2j
http://mynasa.nasa.gov/worldbook/artificial_satellites_worldbook_prt.htm









0 comments:
Post a Comment